International projects: how to adjust your data
To improve early estimates, a consistent approach should be in place to quantify locational impacts on your projects: location factors. Applying relevant location factors over parts of the project allow you to translate the required resources from location to location. These factors have to be updated on a regular basis. In literature, some reference factors can be found for common situations, but to really be effective you will have to develop them yourself from historical project data.
How to approach this problem? The following describes the outline of a location factors study:
1. Making projects comparable
To extract locational influences when comparing projects, you have to keep all other effects constant. Find projects that had a comparable scope and split off the unique parts. For example, comparing the construction of on-shore gas processing plants, some projects might include a jetty or other extra infrastructure. By separating this from the rest of the scope, you make sure that you are indeed comparing apples to apples.
2. Divide the scope in market baskets
Identify and group parts of the project that show a common fluctuation in cost and hours when translating to a different location. Let’s call these groups market baskets. Make a table of the market baskets showing costs versus location. Split the various baskets in the following cost categories to bring in more details when the collected data allows:
a. Equipment and materials
b. Construction labor and engineering staff
c. Supply & Erect contractors and construction equipment
d. Management and supervision
3. Bring costs to the same price level and currency
Probably, the resources for projects have been purchased in different currencies. Translate them into your reference currency using the exchange rate from that time. The next step is to index all costs and bring them to the current price level, taking inflation into account.
4. Start using the factors
The ratio of the different costs and hours now provides the location factor per market basket. These factors have to be updated on a regular basis as the world market, currencies and politics are constantly changing.
The result is an easy applicable set of factor tables. In estimating software that is based on a database, like Cleopatra Enterprise, these tables can be stored in a library and applied to cost estimates to quickly gain insight in the differences in procurement costs between locations and choose the most economical alternative. In the example below we compared equipment procurement costs between different locations worldwide:
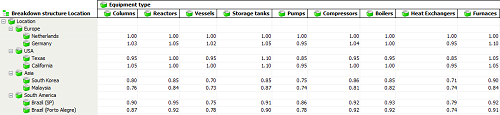
These steps provide a method to break down a project’s scope in market baskets for studying. Next to this, there is virtually an infinite amount of ways cost data can be broken down, analyzed tabulated, or reported. Breakdown structures can also be used to generate all kinds of characteristic values or benchmarks and can become an essential business intelligence tool for a project.
If you have a question or want to know more about CESK data, please feel free to contact us.